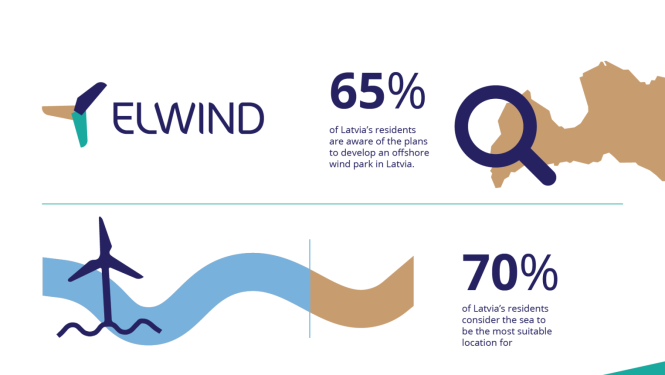
The latest survey data show that public awareness in Latvia about wind park development plans and energy security issues is gradually increasing. For example, 65% of respondents in a survey conducted by Norstat Latvia report that they are at least somewhat informed about the plans to develop offshore wind park in Latvia. At the same time, society increasingly supports a “moderate” development approach – more and more residents believe that Latvia should become an energy-neutral country and…
The latest survey data show that public awareness in Latvia about wind park development plans and energy security issues is gradually increasing. For example, 65% of respondents in a survey conducted by Norstat Latvia report that they are at least somewhat informed about the plans to develop offshore wind park in Latvia. At the same time, society increasingly supports a “moderate” development approach – more and more residents believe that Latvia should become an energy-neutral country and produce only as much electricity as it consumes domestically. A survey commissioned as part of the ELWIND project shows that public awareness of the joint Latvian–Estonian initiative to develop an offshore wind park in the Baltic Sea has increased. This…